

Learn more about natural remedies for epilepsy. Other options, like behavioral therapy and CBD oil, may help with treating drug-resistant epilepsy. Over time, it changes how brain cells work. It works by sending mild electrical pulses through the vagus nerve, which leads to the brain. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): This therapy treats people with focal seizures. These diets should be carried out with support from a registered dietitian. Recommended diets include the modified Atkins diet, ketogenic diet, and low glycemic diet. It involves safely removing the focal point, or the part of the brain where the seizures start.ĭietary changes: Some diets may help control seizures. Surgery: This option typically works best for people who have seizures originating from one part of the brain. Around 33% of adults and 20–25% of children with epilepsy do not respond to their first-line treatment and must consider other options.Ī doctor will discuss various treatments a person can try. This means they cannot control their epilepsy using the first two medications prescribed. Some people have drug-resistant epilepsy. Most people who have epilepsy have a good response to this form of treatment. If the medication does not help someone’s epilepsy, doctors may prescribe a different drug in place of, or combined with, the first medication. Some drugs work for only one type of seizure, while others can control various seizure types.Ī doctor prescribes medications based on a person’s seizure type, medical history, and age. Medicationĭoctors typically use medication to control and stop epileptic seizures. There are different types of treatments for epilepsy. Unknown epilepsy also presents with non-motor symptoms. If they last more than 5 minutes, call emergency services immediately.
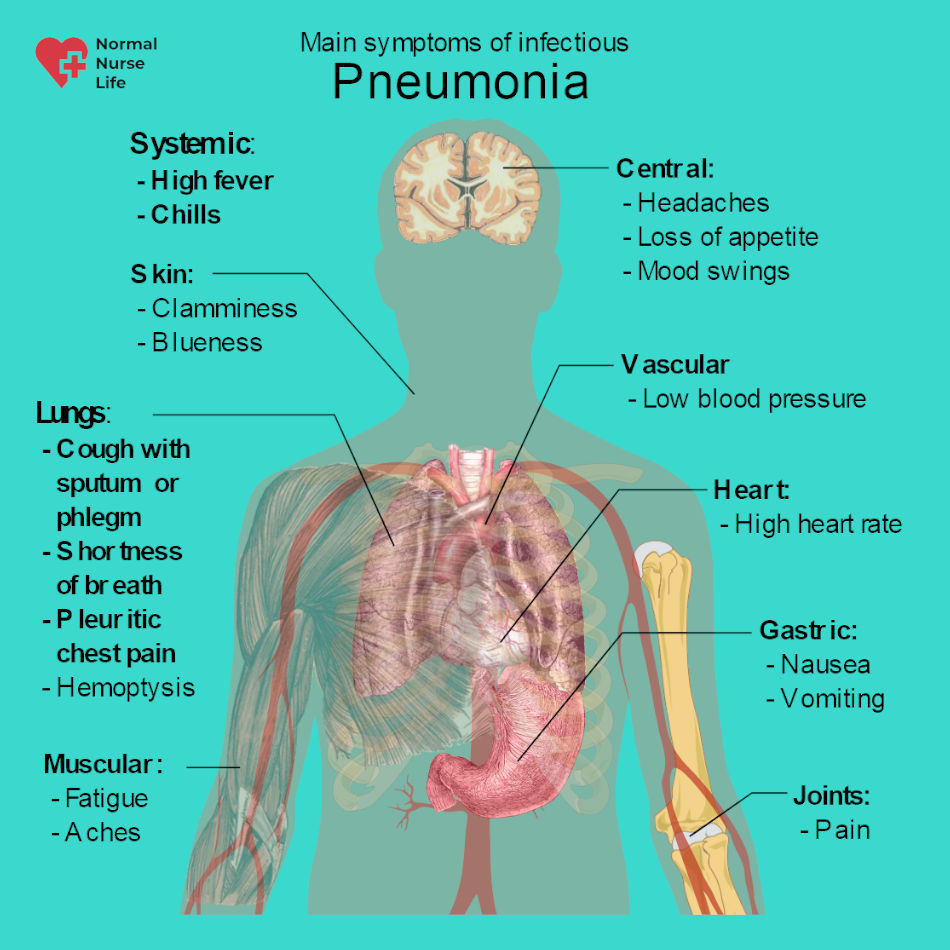
These seizures can have the following symptoms: Motor seizures often present as tonic-clonic (previously referred to as “grand-mal”). People with unknown epilepsy can have a combination of motor and non-motor symptoms. If doctors do not know where seizures originate, they will diagnose a person with unknown epilepsy. Because it is often misdiagnosed, people who think they or a family member may have these seizures should contact a doctor. It is usually caused by a mutation in the SCN1A gene. Therefore, they can experience a mixture of the symptoms discussed above.Ĭombined epilepsy is linked to Dravet syndrome, which is a rare, lifelong form of epilepsy. Someone with combination epilepsy has both generalized seizures and focal seizures. Some non-motor symptoms of focal seizures include: However, they may cause confusion or changes in emotions. Non-motor symptoms do not affect how someone moves. repeated movements, like clapping or chewing.Some motor symptoms of focal seizures include: This can feel like an uneasy feeling in the stomach, similar to the feeling of riding a rollercoaster.Īs the seizure progresses, a person can experience motor and non-motor symptoms. These seizures can begin with an aura, which are minor symptoms signifying the seizure’s onset. They can start in one area and move to others. Unlike generalized seizures, focal seizures only affect one part of the brain. People with focal epilepsy have focal seizures. Generalized epilepsy usually starts during childhood.
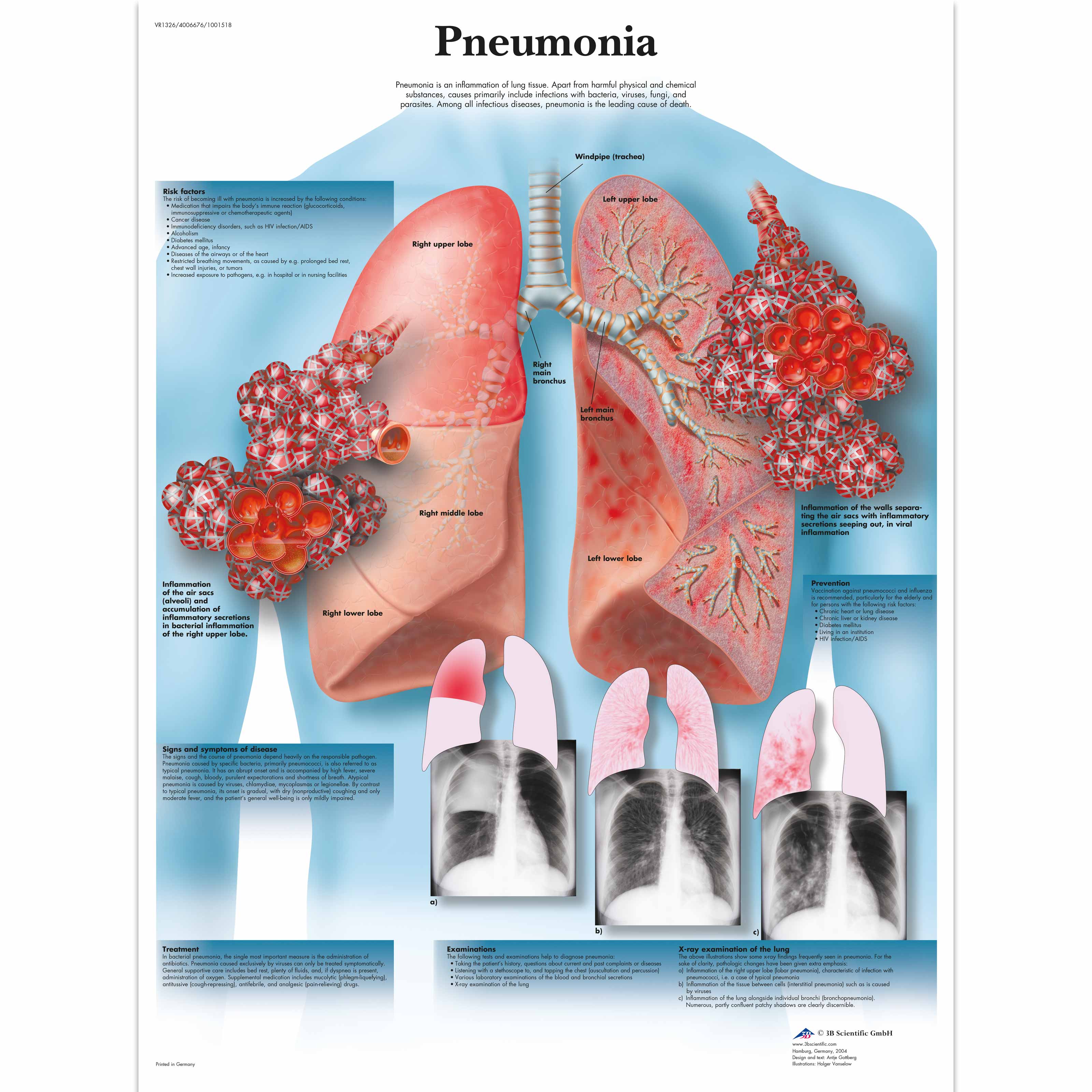
Non-motor seizures are also called absence seizures. If someone has a motor seizure, they may experience: Additionally, these seizures may be either motor, which involve physical movement, or non-motor, which do not. These affect both the left and right sides of the brain. People with this type of epilepsy have generalized seizures. This means they have different identifying factors and treatments. combined generalized and focal epilepsyĮach type of epilepsy affects the brain differently.
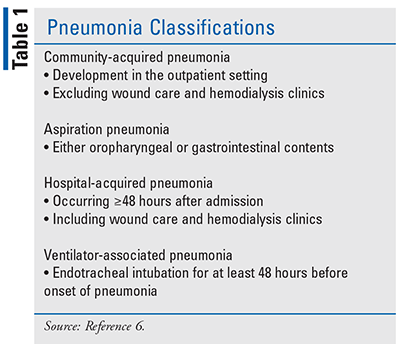
The four different types of epilepsy are defined by the type of seizure a person experiences. A person with epilepsy can experience one or multiple types of seizure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
